CUSTOMER SCENARIO

26-year-old Stephen was referred to the Pharmacy First service for his acute sore throat. After a consultation with the pharmacist, he is supplied with antibiotics for his bacterial throat infection. Stephen is advised that his antibiotics will take a few days to start relieving his symptoms and that he must finish the full antibiotic course.
Stephen is concerned as he is in pain and has an important presentation later at work. He is wondering if there is anything he can use that will work quickly to help reduce the inflammation and pain and that will last until he finishes work (around 6 hours).
You consider the NEW Strefen Spray and confirm the suitability of this product with the pharmacist alongside Stephen’s antibiotics and any medical conditions he has or medicines he may be taking.
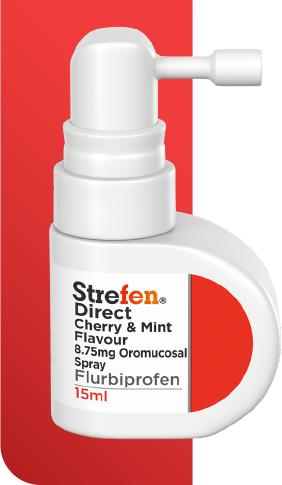
NEW STREFEN SPRAY
You recommend Strefen Spray because compared to other sore throat sprays available: 8-12
There is nothing stronger for targeted relief of a painful throat
It provides rapid relief from 5 minutes and lasts up to 6 hours
It contains flurbiprofen (NSAID), which reduces inflammation and delivers pain relief directly to the sore throat
Its pump delivers a gentle, fine and even mist with every spray, ensuring an accurate dose each time.
DOSE9,13
ADULTS AGED 18 YEARS AND OVER: One dose (3 sprays) administered to the back of the throat every 3-6 hours as required, up to a maximum of 5 doses in a 24-hour period.
This product is for short-term use only and for a maximum of three days, unless otherwise instructed by a doctor.
ADVISING STEPHEN HOW TO USE THE SPRAY9,13
The spray is for oromucosal administration ONLY. It should be sprayed into the throat where it is absorbed into the body via the mucosal tissue.
PRIME THE SPRAY: Before first use, activate the pump by pointing the nozzle away and spraying a minimum of four times until a fine, consistent mist is produced. The pump is then primed and ready for use.
USING THE SPRAY: He should NOT inhale whilst spraying.
-

Rotate the nozzle.
-

Aim the nozzle towards the back of the throat.
-

Using a smooth rapid motion, depress the pump fully 3 times, taking care to fully depress the pump for each spray, whilst removing the finger from the top of the pump between each spray.
BETWEEN DOSES: he should point the nozzle away from him and spray a minimum of once ensuring a fine, consistent mist is produced. Always ensure a fine consistent mist is produced before using the product.
SELF-CARE TIPS
You offer Stephen some self-care tips alongside his treatment:1,5
Take paracetamol alongside his treatment, if required

Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of cool or warm fluids, and avoid very hot drinks

Eat cool, soft foods

Avoid smoking and smoky places

Suck hard sweets, ice cubes or ice lollies

Rest
WATCH THE FOLLOWING VIDEO to understand more about Strefen Spray's targeted spray pump and how it compares to other sprays.
An alternative option to ease sore throat symptoms could be the Strefen lozenge, which has a soothing effect on the throat. It starts to relieve symptoms in 2 minutes and lasts up to 4 hours.7

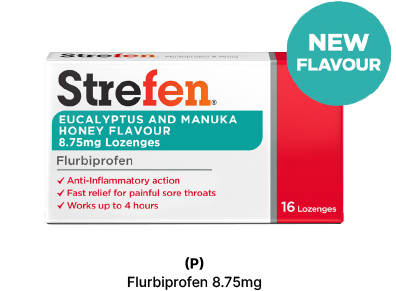
TO LEARN MORE ABOUT STREFEN LOZENGES CLICK HERE
1. NHS. Sore throat. 2024. Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/sore-throat/
2. NICE. Sore throat (acute): antimicrobial prescribing. 2018.
Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng84/resources/sore-throat-acute-antimicrobial-prescribing-pdf-1837694694085
3. NICE. Sore throat - acute: How do I diagnose the cause of a sore throat? 2024.
Available at: https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/sore-throat-acute/diagnosis/diagnosing-the-cause/
4. NHS England. NHS Pharmacy First – Clinical Pathways. 2023.
Available at: https://www.england.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/PRN00936_ii_Pharmacy-First-Clinical-Pathways-v.1.6.pdf
5. NHS inform. Sore throat. 2023. Available at: https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/ears-nose-and-throat/sore-throat/
6. NHS Inform. Coronavirus (COVID-19). 2024.
Available at: https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/infections-and-poisoning/coronavirus-covid-19/coronavirus-covid-19/
7. SmPC. Strefen Honey and Lemon. 2023. Available at: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/6514/smpc/print
8. de Looze F, et al. Eur J Gen Pract 2016; in press
9. SmPC. Strefen Direct Cherry and Mint Flavour 8.75mg Oromucosal Spray. 2024.
Available at: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/15868/smpc#about-medicine
10. Reckitt Data on file
11. Reckitt Data on file
12. Veale D, et al. Comparison of the Characteristics and Performance of Flurbiprofen 8.75 mg Spray for Sore Throat. Curr Drug Deliv. 2017;14(5):725-733.
13. Patient information leaflet. Strefen Direct Cherry and Mint Flavour 8.75mg oromucosal spray. 2024.
Available at: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/files/pil.15868.pdf
Online references last accessed July 2025.
Essential Information: Strefen Direct Cherry and Mint Flavour 8.75mg Oromucosal Spray PL 00063/0715
Active Ingredient(s): One actuation contains 2.92 mg of Flurbiprofen, three actuations equal to one dose contains 8.75mg, corresponding to 16.2 mg/ml Flurbiprofen.
Indications: Strefen Direct Cherry and Mint is indicated for the short term symptomatic relief of acute sore throat in adults.
Dosage & Administration: Posology For short-term use only.
Adults aged 18 years and over: One dose (3 actuations) administered to the back of the throat every 3 6 hours as required, up to a maximum of 5 doses in a 24 hour period. Paediatric population: The safety and efficacy of Strefen Direct Cherry and Mint in children or adolescents under 18 years has not been established. Elderly patients: A general dose recommendation cannot be given, since to date clinical experience is limited. The elderly are at increased risk of the serious consequences of adverse reactions.
The lowest effective dose should be administered for the shortest duration necessary to control symptoms (see section 4.4).
Method of administration: For oromucosal administration. Do not inhale whilst spraying. It is recommended that this product should be used for a maximum of 3 days.
Before first use, activate the pump by pointing the nozzle away from you and spraying a minimum of four times until a fine, consistent mist is produced. The pump is then primed and ready for use. Between each dose point the nozzle away from you and spray a minimum of once ensuring a fine, consistent mist is produced. Always ensure a fine consistent mist is produced before dosing the product.
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1. Patients who have previously shown hypersensitivity reactions (e.g asthma, bronchospasm, rhinitis, angioedema or urticaria) in response to acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs. Active, or history of recurrent peptic ulcer/haemorrhage (two or more distinct episodes of proven ulceration) and intestinal ulceration. History of gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation, severe colitis, haemorrhagic or haematopoietic disorders related to previous NSAID therapy. Last trimester of pregnancy (See section 4.6). Severe heart failure, severe renal failure or severe hepatic failure (see section 4.4). Children and adolescents below 18 years.
Special warnings and precautions for use:
Undesirable effects may be minimised by using the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary to control symptoms.
Infections
Since in isolated cases an exacerbation of infective inflammations (e.g. development of necrotising fasciitis) has been described in temporal association with the use of systemic NSAIDs as a class, the patient is advised to consult a physician immediately if signs of a bacterial infection occur or worsen during the flurbiprofen spray therapy. It should be considered whether initiation of an anti-infective antibiotic therapy is indicated.
In cases of purulent bacterial pharyngitis/tonsillitis, the patient is advised to consult a physician as the treatment needs to be re-evaluated.
Masking of symptoms of underlying infections: Epidemiological studies suggest that systemic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can mask symptoms of infection, which may lead to delayed initiation of appropriate treatment and thereby worsening the outcome of the infection. This has been observed in bacterial community acquired pneumonia and bacterial complications to varicella. When Strefen Direct Cherry and Mint Flavour 8.75mg Oromucosal Spray is administered while the patient suffers from fever or pain in relation to infection, monitoring of infection is advised.
Treatment should be administered for three days maximum.
If the symptoms get worse or if new symptoms occur, the treatment should be re-evaluated.
If mouth irritation occurs, flurbiprofen treatment should be withdrawn.
Elderly population
The elderly have an increased frequency of adverse reactions to NSAIDs especially gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation which may be fatal.
Respiratory
Bronchospasm may be precipitated in patients suffering from or with a previous history of bronchial asthma or allergic disease. Flurbiprofen spray should be used with caution in these patients.
Other NSAIDs
The use of flurbiprofen spray with concomitant NSAIDs including cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors should be avoided (see section 4.5).
Systemic lupus erythematosus and mixed connective tissue disease
Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and mixed connective tissue disease may have an increased risk of aseptic meningitis (see section 4.8), however this effect is not usually seen with short term limited use products such as flurbiprofen spray.
Cardiovascular, Renal and Hepatic Impairment
NSAIDs have been reported to cause nephrotoxicity in various forms including interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome and renal failure. The administration of an NSAID may cause a dose dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and precipitate renal failure. Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, cardiac impairment, liver dysfunction, those taking diuretics and the elderly, however, this effect is not usually seen with short term, limited use products such as flurbiprofen spray.
Hepatic
Mild to moderate hepatic dysfunction (see sections 4.3 and 4.8).
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular effects
Caution (talk with doctor or pharmacist) is required prior to starting treatment in patients with a history of hypertension and/or heart failure as fluid retention, hypertension and oedema have been reported in association with NSAID therapy.
Clinical trial and epidemiological data suggest that use of some NSAIDs, (particularly at high doses and in long term treatment) may be associated with a small increased risk of arterial thrombotic events (for example myocardial infarction or stroke). There are insufficient data to exclude such a risk for flurbiprofen when given at a daily dose of no more than 5 doses (3 sprays per dose).
Nervous System effects
Analgesic induced headache - In the event of prolonged use of analgesics or use beyond the regulations headache may occur, which must not be treated with increased doses of the medicinal product.
Gastrointestinal
NSAIDs should be given with care to patients with a history of gastrointestinal disease (ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease) as these conditions may be exacerbated (see section 4.8). Gastrointestinal bleeding, ulceration or perforation, which can be fatal, has been reported with all NSAIDs at anytime during treatment, with or without warning symptoms or a previous history of serious GI events.
The risk of GI bleeding, ulceration or perforation is higher with increasing NSAID doses, in patients with a history of ulcer, particularly if complicated with haemorrhage or perforation (see section 4.3), and in the elderly, however this effect is not usually seen with short term limited use products such as flurbiprofen spray. Patients with a history of GI toxicity, particularly when elderly, should report any unusual abdominal symptoms (especially GI bleeding) to their healthcare professional.
Caution should be advised in patients receiving concomitant medications which could increase the risk of ulceration or bleeding, such as oral corticosteroids, anticoagulants such as warfarin, selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors or anti-platelet agents such as acetylsalicylic acid (see section 4.5).
If GI bleeding or ulceration occurs in patients receiving flurbiprofen, the treatment should be withdrawn.
Haematological effects
Flurbiprofen, like other NSAIDs, may inhibit platelet aggregation and prolong bleeding time. Flurbiprofen spray should be used with caution in patients with a potential for abnormal bleeding.
Dermatological
Serious skin reactions, some of them fatal, including exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, have been reported very rarely in association with the use of NSAIDs (see section 4.8). Flurbiprofen spray should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash, mucosal lesions, or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
This product contains methyl parahydroxybenzoate and propyl parahydroxybenzoate which may cause allergic reactions (possibly delayed).
This medicine contains fragrance with Citral, d-Limonene, Eugenol and Linalool. Citral, d-Limonene, Eugenol and Linalool may cause allergic reactions.
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per dose, that is to say essentially ‘sodium-free’.
Fertility, Pregnancy and Lactation:
Pregnancy
Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis may adversely affect the pregnancy and/or the embryo/foetal development. Data from epidemiological studies suggest an increased risk of miscarriage and of cardiac malformation and gastroschisis after use of a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor in early pregnancy. The absolute risk for cardiovascular malformation was increased from less than 1%, up to approximately 1.5 %. The risk is believed to increase with dose and duration of therapy. In animals, administration of a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor has been shown to result in increased pre- and post-implantation loss and embryo-foetal lethality. In addition, increased incidences of various malformations, including cardiovascular, have been reported in animals given a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor during the organogenetic period. During the first and second trimester of pregnancy, flurbiprofen should not be given.
During the third trimester of pregnancy, all prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors may expose
-
the foetus to:
cardiopulmonary toxicity (with premature closure of the ductus arteriosus and pulmonary hypertension);
renal dysfunction, which may progress to renal failure with oligo-hydroamniosis;
-
the mother and the neonate, at the end of pregnancy, to:
possible prolongation of bleeding time, an anti-aggregating effect which may occur even at very low doses.
inhibition of uterine contractions resulting in delayed or prolonged labour.
Consequently, flurbiprofen is contraindicated during the third trimester of pregnancy (see section 4.3).
Breastfeeding
In limited studies, flurbiprofen appears in the breast milk in very low concentration and is unlikely to affect the breast-fed infant adversely. However, because of possible adverse effects of NSAIDs on breast-fed infants, flurbiprofen spray is not recommended for use in nursing mothers.
Fertility
There is some evidence that drugs which inhibit cyclo-oxygenase/ prostaglandin synthesis may cause impairment of female fertility by an effect on ovulation. This is reversible on withdrawal of treatment.
Side effects:
Hypersensitivity reactions to NSAIDs have been reported and these may consist of:
(a) Non-specific allergic reactions and anaphylaxis
(b) Respiratory tract reactivity, e.g. asthma, aggravated asthma, bronchospasm, dyspnoea
(c) Various skin reactions, e.g. pruritus, urticaria, angioedema and more rarely exfoliative and bullous dermatoses (including epidermal necrolysis and erythema multiforme).
Oedema, hypertension and cardiac failure have been reported in association with NSAID treatment. There is insufficient data to exclude such a risk for flurbiprofen oromucusal spray, solution.
The following list of adverse effects relates to those experienced with flurbiprofen at OTC doses for short-term use.
(Very common (≥1/10), Common (≥1/100 to <1/10), Uncommon (≥1/1000 to <1/100), Rare (≥1/10000 to <1/1000), Very rare (<1/10000), not known (cannot be estimated from the available data))
Blood and lymphatic system disorders:
Not known: anaemia, thrombocytopenia.
Cardiac and vascular disorders:
Not known: Oedema, hypertension, cardiac failure
Nervous System disorders:
Common: dizziness, headache, parasthesia
Uncommon: somnolence
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders:
Common: throat irritation
Uncommon: exacerbation of asthma and bronchospasm, dyspnoea, wheezing, oropharyngeal blistering, pharyngeal hypoaesthesia.
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Common: diarrhoea, mouth ulceration, nausea, oral pain, paraesthesia oral, oropharyngeal pain, oral discomfort (warm or burning feeling or tingling of the mouth).
Uncommon: abdominal distension, abdominal pain, constipation, dry mouth, dyspepsia, flatulence, glossodynia, dysgeusia, oral dysaesthesia, vomiting
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:
Uncommon: various skin rashes, pruritus.
Not known: severe forms of skin reaction such as bullous reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
General disorders and administration site conditions:
Uncommon: pyrexia, pain
Immune System disorders:
Rare: anaphylactic reaction
Psychiatric disorders:
Uncommon: insomnia
Hepatobiliary disorders:
Not known: hepatitis
Legal Classification: P
Licence Holder: Reckitt Benckiser Healthcare (UK) Ltd, 103-105 Bath Road, Slough, SL1 3UH
Licence Number: PL 00063/0715
Price (ex VAT): £7.99
Last Revised: 01/08/2024
Essential Information: Strefen Honey and Lemon
Active Ingredient(s): Flurbiprofen 8.75mg
Indications: Strefen Honey and Lemon are indicated for the short term symptomatic relief of sore throat in adults and children over the age of 12 years.
Dosage & Administration:
Posology Adults the elderly and children over the age of 12 years: One lozenge sucked/dissolved slowly in the mouth every 3 - 6 hours as required. Maximum 5 lozenges in a 24 hour period. It is recommended that this product should be used for a maximum of three days. Children: Not indicated for children under 12 years.
Elderly: A general dose recommendation cannot be given, since to date clinical experience is limited. The elderly are at increased risk of the serious consequences of adverse reactions.
Impaired hepatic: In patients with mild to moderate impairment of hepatic function no dose reduction is required. In patients with severe hepatic insufficiency flurbiprofen is contraindicated (see section 4.3). Impaired renal: In patients with mild to moderate impairment of renal function no dose reduction is required. In patients with severe renal insufficiency flurbiprofen is contraindicated (see section 4.3).
Method of administration: For oromucosal administration and short-term use only. As with all lozenges, to avoid local irritation, Strefen Honey and Lemon should be moved around the mouth whilst sucking. The lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest duration necessary to relieve symptoms (see section 4.4)
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to flurbiprofen or any of the excipients in the product. Patients who have previously shown hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. asthma, bronchospasm, rhinitis, angioedema, or urticaria) in response to acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs. Active or history of recurrent peptic ulcer/haemorrhage (two or more distinct episodes of proven ulceration) and intestinal ulceration. History of gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation, severe colitis, haemorrhagic or haematopoietic disorders related to previous NSAID therapy. Last trimester of pregnancy. (See section 4.6) Severe heart failure, severe renal failure or severe hepatic failure (see section 4.4)
Special warnings and precautions for use: Undesirable effects may be minimised by using the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary to control symptoms.
Elderly population: The elderly have an increased frequency of adverse reactions to NSAIDs, especially gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation, which may be fatal.
Respiratory: Bronchospasm may be precipitated in patients suffering from, or with a previous history of bronchial asthma or allergic disease. Flurbiprofen lozenges should be used with caution in these patients.
Other NSAIDs: The use of flurbiprofen lozenges with concomitant NSAIDs including cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors should be avoided (see section 4.5).
Systemic lupus erythematosus and mixed connective tissue disease: Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and mixed connective tissue disease may have an increased risk of aseptic meningitis (see section 4.8), however this effect is not usually seen with short term limited use products such as flurbiprofen lozenges.
Cardiovascular, Renal and Hepatic Impairment: NSAIDs have been reported to cause nephrotoxicity in various forms including interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome and renal failure. The administration of an NSAID may cause a dose dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and precipitate renal failure. Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, cardiac impairment, liver dysfunction, those taking diuretics and the elderly, however, this effect is not usually seen with short term, limited use products such as flurbiprofen lozenges.
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular effects: Caution (discussion with doctor or pharmacist) is required prior to starting treatment in patients with a history of hypertension and/or heart failure as fluid retention, hypertension and oedema have been reported in association with NSAID therapy. Clinical trial and epidemiological data suggest that the use of NSAIDs (particularly at high doses and in long term treatment) may be associated with a small increased risk of arterial thrombotic events (for example myocardial infarction or stroke). There are insufficient data to exclude such a risk for flurbiprofen when given at a daily dose of no more than 5 lozenges.
Hepatic: Mild to moderate hepatic dysfunction (see sections 4.3 and 4.8)
Nervous System effects: Analgesic induced headache - In the event of prolonged use of analgesics or use beyond the regulations headache may occur, which must not be treated with increased doses of the medicinal product.
Gastrointestinal: NSAIDs should be given with care to patients with a history of gastrointestinal disease (ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease) as these conditions may be exacerbated (see section 4.8). Gastrointestinal bleeding, ulceration or perforation, which can be fatal has been reported with all NSAIDs at anytime during treatment, with or without warning symptoms or a previous history of serious GI events. The risk of GI bleeding, ulceration or perforation is higher with increasing NSAID doses, in patients with a history of ulcer, particularly if complicated with haemorrhage or perforation (see Section 4.3), and in the elderly, however this effect is not usually seen with short term limited use products such as flurbiprofen lozenges. Patients with a history of GI toxicity, particularly the elderly, should report any unusual abdominal symptoms (especially GI bleeding) to their healthcare professional. Caution should be advised in patients receiving concomitant medications which could increase the risk of ulceration or bleeding, such as oral corticosteroids, anticoagulants such as warfarin, selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors or anti-platelet agents such as acetylsalicylic acid (see section 4.5). If GI bleeding or ulceration occurs in patients receiving flurbiprofen, the treatment should be withdrawn.
Dermatological: Serious skin reactions, some of them fatal, including exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, have been reported very rarely in association with the use of NSAIDSs (see section 4.8). Flurbiprofen lozenges should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash, mucosal lesions, or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
Infections: Since in isolated cases an exacerbation of infective inflammations (e.g. development of necrotising fasciitis) has been described in temporal association with the use of systemic NSAIDs as a class, the patient is advised to consult a physician immediately if signs of a bacterial infection occur or worsen during the flurbiprofen lozenges therapy. It should be considered whether initiation of an anti-infective antibiotic therapy is indicated.
Masking of symptoms of underlying infections: Epidemiological studies suggest that systemic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can mask symptoms of infection, which may lead to delayed initiation of appropriate treatment and thereby worsening the outcome of the infection. This has been observed in bacterial community acquired pneumonia and bacterial complications to varicella. When Strefen Honey and Lemon is administered while the patient suffers from fever or pain in relation to infection, monitoring of infection is advised.
Important Information about some of the ingredients of this medicine
This medicine contains only very low levels of gluten (from wheat starch). It is regarded as ‘gluten-free’ and is very unlikely to cause problems if you have coeliac disease. One lozenge contains no more than 21.38 micrograms of gluten. If you have wheat allergy (different from coeliac disease) you should not take this medicine.
This medicine contains 1.407 g Sucrose per lozenge and 1.069 g Glucose per lozenge. Patients with rare hereditary problems of fructose intolerance, glucose galactose malabsorption or sucrase isomaltase insufficiency should not take this medicine.
This medicine contains sulphites, which may rarely cause severe hypersensitivity reactions and bronchospasm.
This medicine contains fragrance with Citral, Citronellol, d-Limonene, Farnesol, Geraniol and Linalool. Citral, Citronellol, d-Limonene, Farnesol, Geraniol and Linalool may cause allergic reactions.
This medicine contains Butylated hydroxyanisole (E320) (present in Lemon flavour) which may cause local skin reactions (e.g. contact dermatitis), or irritation to the eyes and mucous membranes.
Fertility, Pregnancy and Lactation:
Pregnancy
Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis may adversely affect the pregnancy and/or the embryo/foetal development. Data from epidemiological studies suggest an increased risk of miscarriage and of cardiac malformation and gastroschisis after use of a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor in early pregnancy. The absolute risk for cardiovascular malformation was increased from less than 1%, up to approximately 1.5 %. The risk is believed to increase with dose and duration of therapy. In animals, administration of a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor has been shown to result in increased pre- and post-implantation loss and embryo-foetal lethality. In addition, increased incidences of various malformations, including cardiovascular, have been reported in animals given a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor during the organogenetic period. During the first and second trimester of pregnancy, flurbiprofen should not be given unless clearly necessary. If flurbiprofen is used by a woman attempting to conceive, or during the first and second trimester of pregnancy, the dose should be kept as low and duration of treatment as short as possible.
During the third trimester of pregnancy, all prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors may expose
-
the foetus to:
cardiopulmonary toxicity (with premature closure of the ductus arteriosus and pulmonary hypertension).
renal dysfunction, which may progress to renal failure with oligo-hydroamniosis;
-
the mother and the neonate, at the end of pregnancy, to:
possible prolongation of bleeding time, an anti-aggregating effect which may occur even at very low doses.
inhibition of uterine contractions resulting in delayed or prolonged labour.
Consequently, flurbiprofen is contraindicated during the third trimester of pregnancy.
Lactation
In limited studies, flurbiprofen appears in the breast milk in very low concentration and is unlikely to affect the breast-fed infant adversely. However, because of possible adverse effects of NSAIDs on breast-fed infants, Strefen Honey & Lemon lozenges are not recommended for use in nursing mothers.
Fertility
There is some evidence that drugs which inhibit cyclo-oxygenase/ prostaglandin synthesis may cause impairment of female fertility by an effect on ovulation. This is reversible on withdrawal of treatment.
Side effects:
Hypersensitivity reactions to NSAIDs have been reported and these may consist of:
(a) non-specific allergic reactions and anaphylaxis
(b) respiratory tract reactivity e.g. asthma, aggravated asthma, bronchospasm, dyspnoea
(c) various skin reactions e.g. pruritus, urticaria, angioedema and more rarely exfoliative and bullous dermatoses (including epidermal necrolysis and erythema multiforme)
Oedema, hypertension and cardiac failure have been reported in association with NSAID treatment. Clinical trial and epidemiological data suggest that use of some NSAIDs, (particularly at high doses and in long term treatment) may be associated with a small increased risk of arterial thrombotic events (for example myocardial infarction or stroke), (see section 4.4). There is insufficient data to exclude such a risk for flurbiprofen 8.75 mg lozenges
The following list of adverse effects relates to those experienced with flurbiprofen at OTC doses for short-term use.
(Very common (≥1/10), Common (≥1/100 to <1/10), Uncommon (≥1/1000 to <1/100), Rare (≥1/10000 to <1/1000), Very rare (<1/10000), not known (cannot be estimated from the available data))
Blood and lymphatic system disorders:
Not known: anaemia, thrombocytopenia.
Immune System disorders:
Rare: anaphylactic reaction
Psychiatric disorders:
Uncommon: insomnia
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disorders:
Not known: Oedema, hypertension and cardiac failure
Nervous System disorders:
Common: dizziness, headache, parasthesia
Uncommon: somnolence
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders:
Common: throat irritation
Uncommon: exacerbation of asthma and bronchospasm, dyspnoea, wheezing, oropharyngeal blistering, pharyngeal hypoaesthesia.
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Common: diarrhoea, mouth ulceration, nausea, oral pain, paraesthesia oral, oropharyngeal pain, oral discomfort (warm or burning feeling or tingling of the mouth).
Uncommon: abdominal distension, abdominal pain, constipation, dry mouth, dyspepsia, flatulence, glossodynia, dysgeusia, oral dysaesthesia, vomiting.
Hepatobiliary disorders:
Not known: hepatitis
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:
Uncommon: various skin rashes, pruritus.
Not known: severe forms of skin reaction such as bullous reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
General disorders and administration site conditions:
Uncommon: pyrexia, pain
Legal Classification: P
Licence Holder: Reckitt Benckiser Healthcare (UK) Ltd, 103-105 Bath Road, Slough, Berkshire, SL1 3UH, United Kingdom
Licence Number: PL 00063/0714
Price (ex VAT): £6.99
Last Revised: 01/11/2023.
Essential Information: Strefen Eucalyptus and Manuka Honey Flavour 8.75mg Lozenges
Active Ingredient(s): Flurbiprofen 8.75mg
Indications: Strefen Eucalyptus and Manuka Honey Flavour 8.75mg Lozenges are indicated for the short term symptomatic relief of sore throat in adults and adolescents over the age of 12 years.
Dosage & Administration:
Posology The lowest effective dose should be administered for the shortest duration necessary to control symptoms (see section 4.4). Adults and adolescents over the age of 12 years: One lozenge sucked/dissolved slowly in the mouth every 3-6 hours as required. Maximum 5 lozenges in a 24 hour period. It is recommended that this product should be used for a maximum of three days. Children: Not indicated for children under 12 years. Elderly: A general dose recommendation cannot be given, since to date clinical experience is limited. The elderly are at increased risk of the serious consequences of adverse reactions.
Impaired hepatic: In patients with mild to moderate impairment of hepatic function no dose reduction is required. In patients with severe hepatic insufficiency flurbiprofen is contraindicated (see section 4.3). Impaired renal: In patients with mild to moderate impairment of renal function no dose reduction is required. In patients with severe renal insufficiency flurbiprofen is contraindicated (see section 4.3).
Method of administration: For oromucosal administration and short-term use only. As with all lozenges, to avoid local irritation, Strefen Eucalyptus and Manuka Honey Flavour 8.75mg Lozenges should be moved around the mouth whilst sucking.
Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity to flurbiprofen or any of the excipients listed in section 6.1.
Patients who have previously shown hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. asthma, bronchospasm, rhinitis, angioedema or urticaria) in response to acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs.
Active, or history of recurrent peptic ulcer/haemorrhage (two or more distinct episodes of proven ulceration) and intestinal ulceration.
History of gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation, severe colitis, haemorrhagic or haematopoietic disorders related to previous NSAID therapy.
Last trimester of pregnancy (See section 4.6)
Severe heart failure, severe renal failure or severe hepatic failure (see section 4.4).
Special warnings and precautions for use: Undesirable effects may be minimized by using the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary to control symptoms
Elderly population: The elderly have an increased frequency of adverse reactions to NSAIDs especially gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation which may be fatal.
Respiratory: Bronchospasm may be precipitated in patients suffering from or with a previous history of bronchial asthma or allergic disease. Flurbiprofen lozenges should be used with caution in these patients
Other NSAIDs: The use of flurbiprofen lozenges with concomitant NSAIDs including cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors should be avoided (see section 4.5).
Systemic lupus erythematosus and mixed connective tissue disease: Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and mixed connective tissue disease may have an increased risk of aseptic meningitis (see section 4.8), however this effect is not usually seen with short term limited use products such as flurbiprofen lozenges.
Cardiovascular, Renal and Hepatic Impairment: NSAIDs have been reported to cause nephrotoxicity in various forms including interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome and renal failure. The administration of an NSAID may cause a dose dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and precipitate renal failure. Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, cardiac impairment, liver dysfunction, those taking diuretics and the elderly, however, this effect is not usually seen with short term, limited use products such as flurbiprofen lozenges.
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular effects: Caution (discussion with doctor or pharmacist) is required prior to starting treatment in patients with a history of hypertension and/or heart failure as fluid retention, hypertension and oedema have been reported in association with NSAID therapy. Clinical trial and epidemiological data suggest that use of some NSAIDs, (particularly at high doses and in long term treatment) may be associated with a small increased risk of arterial thrombotic events (for example myocardial infarction or stroke). There are insufficient data to exclude such a risk for flurbiprofen when given at a daily dose of no more than 5 lozenges.
Hepatic: Mild to moderate hepatic dysfunction (see sections 4.3 and 4.8)
Nervous System effects Analgesic induced headache - In the event of prolonged use of analgesics or use beyond the regulations headache may occur, which must not be treated with increased doses of the medicinal product.
Gastrointestinal: NSAIDs should be given with care to patients with a history of gastrointestinal disease (ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease) as these conditions may be exacerbated (see section 4.8). Gastrointestinal bleeding, ulceration or perforation, which can be fatal, has been reported with all NSAIDs at anytime during treatment, with or without warning symptoms or a previous history of serious GI events. The risk of GI bleeding, ulceration or perforation is higher with increasing NSAID doses, in patients with a history of ulcer, particularly if complicated with haemorrhage or perforation (see section 4.3), and in the elderly, however this effect is not usually seen with short term limited use products such as flurbiprofen lozenges. Patients with a history of GI toxicity, particularly when elderly, should report any unusual abdominal symptoms (especially GI bleeding) to their healthcare professional. Caution should be advised in patients receiving concomitant medications which could increase the risk of ulceration or bleeding, such as oral corticosteroids, anticoagulants such as warfarin, selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors or anti-platelet agents such as acetylsalicylic acid (see section 4.5). If GI bleeding or ulceration occurs in patients receiving flurbiprofen, the treatment should be withdrawn.
Dermatological: Serious skin reactions, some of them fatal, including exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, have been reported very rarely in association with the use of NSAIDs (see section 4.8). Flurbiprofen lozenges should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash, mucosal lesions, or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
Lactation and Impaired Female Fertility: See section 4.6
Infections: Since in isolated cases an exacerbation of infective inflammations (e.g. development of necrotising fasciitis) has been described in temporal association with the use of systemic NSAIDs as a class, the patient is advised to consult a physician immediately if signs of a bacterial infection occur or worsen during the flurbiprofen lozenges therapy. It should be considered whether initiation of an anti-infective antibiotic therapy is indicated. In cases of purulent bacterial pharyngitis/tonsillitis, the patient is advised to consult a physician as the treatment needs to be re-evaluated.
Masking of symptoms of underlying infections: Epidemiological studies suggest that systemic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can mask symptoms of infection, which may lead to delayed initiation of appropriate treatment and thereby worsening the outcome of the infection. This has been observed in bacterial community acquired pneumonia and bacterial complications to varicella. When Strefen Eucalyptus and Manuka Honey Flavour 8.75mg Lozenges is administered while the patient suffers from fever or pain in relation to infection, monitoring of infection is advised. Treatment should be administered for three days maximum.
Haematological effects: Flurbiprofen, like other NSAIDs, may inhibit platelet aggregation and prolong bleeding time. Flurbiprofen lozenges should be used with caution in patients with a potential for abnormal bleeding.
Sugar intolerance: Patients with rare hereditary problems of fructose intolerance should not take this medicine. If the symptoms get worse or if new symptoms occur, the treatment should be re-evaluated. If mouth irritation occurs, treatment should be withdrawn.
Other warnings: Contains Isomalt and Maltitol which may have a mild laxative effect after multiple daily doses. Isomalt and Maltitol have a calorific value of 2.3 kcal/g. This medicine contains fragrance Anise Alcohol, Benzyl Alcohol, Benzyl Benzoate, Benzyl Cinnamate, Benzyl Salicylate, Cinnamal, Cinnamyl Alcohol, Citral, Geraniol, Limonene and Linalool. Anise Alcohol, Benzyl Alcohol, Benzyl Benzoate, Benzyl Cinnamate, Benzyl Salicylate, Cinnamal, Cinnamyl Alcohol, Citral, Geraniol, Limonene and Linalool may cause allergic reactions.
Fertility, Pregnancy and Lactation:
Pregnancy
Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis may adversely affect the pregnancy and/or the embryo/foetal development. Data from epidemiological studies suggest an increased risk of miscarriage and of cardiac malformation and gastroschisis after use of a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor in early pregnancy. The absolute risk for cardiovascular malformation was increased from less than 1%, up to approximately 1.5%. The risk is believed to increase with dose and duration of therapy. In animals, administration of a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor has been shown to result in increased pre- and post-implantation loss and embryo-foetal lethality. In addition, increased incidences of various malformations, including cardiovascular, have been reported in animals given a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor during the organogenetic period. During the first and second trimester of pregnancy, flurbiprofen should not be given unless clearly necessary. If flurbiprofen is used by a woman attempting to conceive, or during the first and second trimester of pregnancy, the dose should be kept as low and duration of treatment as short as possible.
During the third trimester of pregnancy, all prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors may expose
-
the foetus to:
cardiopulmonary toxicity (with premature closure of the ductus arteriosus and pulmonary hypertension);
renal dysfunction, which may progress to renal failure with oligo-hydroamniosis;
-
the mother and the neonate, at the end of pregnancy, to:
possible prolongation of bleeding time, an anti-aggregating effect which may occur even at very low doses.
inhibition of uterine contractions resulting in delayed or prolonged labour.
Consequently, flurbiprofen is contraindicated during the third trimester of pregnancy (see section 4.3).
Breast-feeding
In limited studies, flurbiprofen appears in the breast milk in very low concentration and is unlikely to affect the breast-fed infant adversely. However, because of possible adverse effects of NSAIDs on breast-fed infants, Strefen Eucalyptus and Manuka Honey Flavour 8.75mg Lozenges are not recommended for use in nursing mothers (see section 4.4).
Fertility
There is some evidence that drugs which inhibit cyclo-oxygenase/ prostaglandin synthesis may cause impairment of female fertility by an effect on ovulation. This is reversible on withdrawal of treatment.
Side effects:
Hypersensitivity reactions to NSAIDs have been reported and these may consist of:
(a) Non – specific allergic reactions and anaphylaxis
(b) Respiratory tract reactivity, e.g. asthma, aggravated asthma, bronchospasm, dyspnoea
(c) Various skin reactions, e.g. pruritus, urticaria, angioedema and more rarely exfoliative and bullous dermatoses (including epidermal necrolysis and erythema multiforme).
Oedema, hypertension and cardiac failure have been reported in association with NSAID treatment. Clinical trial and epidemiological data suggest that the use of some NSAIDs, (particularly at high doses and in long term treatment) may be associated with a small increased risk of arterial thrombotic events (for example myocardial infarction or stroke), (see section 4.4). There is insufficient data to exclude such a risk for Flurbiprofen 8.75 mg lozenges.
The following list of adverse effects relates to those experienced with flurbiprofen at OTC doses for short-term use. Adverse events which have been associated with flurbiprofen are given below, tabulated by system organ class and frequency. Frequencies are defined as: (Very common (≥1/10), Common (≥1/100 to <1/10), Uncommon (≥1/1000 to <1/100), Rare (≥1/10000 to <1/1000), Very rare (<1/10000), not known (cannot be estimated from the available data))
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders:
Not known: Anaemia, thrombocytopenia
Immune System Disorders:
Rare: Anaphylactic reaction
Not known: Hypersensitivity
Psychiatric Disorders:
Uncommon: Insomnia
Nervous System Disorders:
Common: Dizziness, headache, paraesthesia
Uncommon: Somnolence
Cardiac disorders:
Not known: Cardiac failure, oedema
Vascular disorders:
Not known: Hypertension
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders:
Common: Throat irritation
Uncommon: Exacerbation of asthma and bronchospasm, dyspnoea, oropharyngeal blistering, pharyngeal hypoaesthesia
Gastrointestinal Disorders:
Common: Diarrhoea, mouth ulceration, nausea, oral pain, paraesthesia oral, oropharyngeal pain, oral discomfort (warm and burning feeling or tingling in the mouth)
Uncommon: Abdominal distension, abdominal pain, constipation, dry mouth, dyspepsia, flatulence, glossodynia, dysgeusia, oral dysaesthesia, vomiting
Hepatobiliary Disorders:
Not known: Hepatitis
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders:
Uncommon: Pruritus
Not known: Severe forms of skin reaction such as bullous reactions, including Stevens- Johnson Syndrome, erythema multiform and toxic epidermal necrolysis
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions:
Uncommon: Pyrexia, pain
Legal Classification: P
Licence Holder: Reckitt Benckiser Healthcare (UK) Ltd, 103-105 Bath Road, Slough, SL1 3UH, United Kingdom
Licence Number: PL 00063/0767
Price (ex VAT): £6.99
Last Revised: 29/02/2024
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the risk/benefit balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via the Yellow Card Scheme at: www.mhra.gov.uk/yellowcard or search for MHRA Yellow Card in the Google Play or Apple App Store.
